
MS Access As A Dev Tool
Access continues to be a highly efficient tool for business database development.
The Best Microsoft Access Database Solutions owner, consultant, and principal programmer is Alison Balter - a recognized expert Microsoft Access consultant. Alison is the author of 15 Microsoft Access training books and videos. She is a frequent guest speaker at MS Access conferences snd has developed hundreds of applications for businesses of all types.
We know your business data is important; we listen to your concerns, ask questions, and gather information from all stakeholders. We discuss your needs and requirements for your database. We find out what you want, why you need various features so we can obtain as much information as possible. Once we have the information we need, we work with you to design the proper database architecture, plus the dashboards, the questions (queries), forms, and reports you need for an excellent database system.

We also create websites designed for speed to display your data accurately, using ASP.NET technology. Fast, secure, and robust, our ASP.NET websites and web applications give you true business tool for finding and displaying information dynamically on the web.








Access continues to be a highly efficient tool for business database development.
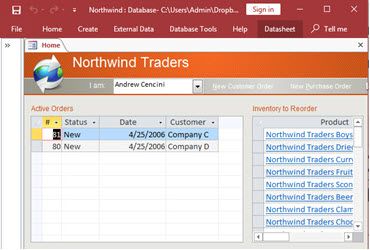
How to create a Microsoft Access application with some unique tips and tricks.
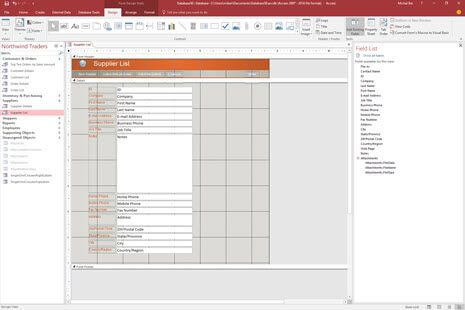
Your Access developer near me has some great info for you about using Access efficiently.
Microsoft Access is a desktop relational database management system included in the Microsoft Office suite. It allows users to design tables, construct queries, and create forms without requiring extensive programming knowledge. For more advanced applications, Access can serve as a front-end interface, utilizing Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) and integrating with other Microsoft programs like Excel, Word, and SQL Server.
Microsoft Access is a desktop relational database management system (RDBMS) designed for practical business use. At its core, Access stores information in structured tables that can be linked together by relationships. This means you can separate your data into logical groups—customers, orders, products—and c onnect them using primary and foreign keys. That's how relational databases work, and Access follows the same fundamental design principles used in larger platforms like SQL Server.
What makes Access useful is its combination of data storage and user interface tools. You can build forms to enter data, create queries to analyze it, and generate reports to share results, all in the same environment. Tables are where the raw data lives. Relationships define how the tables interact. Queries pull information based on conditions, sorting, or grouping. Forms give users a controlled way to enter and review data. Reports let you present summaries or printouts in a structured format.
Access enforces data integrity through rules like referential integrity and field validation. If one table relies on another—such as an Orders table needing a valid Customer ID—Access makes sure that connection is respected. That's important. It prevents orphaned records and keeps the database reliable over time.
Access isn't just for single users. When split into a front-end and back-end design, it can support multiple users across a network. The back-end holds the tables; the front-end contains the forms, queries, and reports. You can also link Access to external data sources like SQL Server or Excel, which adds flexibility without giving up control over the interface.
Access 1.0 was released in November 1992, providing a graphical user interface that simplified database management tasks. This initial version introduced Access Basic, enabling users to automate processes within their databases. Despite its innovative features, Access 1.0 faced performance and compatibility issues. In 1994, Access 2.0 addressed many of these concerns, offering improved functionality and support for larger databases.
With the release of Windows 95, Access 95 (Version 7.0) was introduced, aligning with the new operating system's features. This version integrated the Jet Database Engine, enhancing data storage and query execution capabilities. Access 97 (Version 8.0) followed, incorporating internet features and improved data access pages, reflecting the growing importance of web integration.
Access 2000 (Version 9.0) marked a significant step by introducing data access pages, allowing users to publish database content on the internet. This version also strengthened integration with other Microsoft Office applications, facilitating seamless data exchange. Access 2003 (Version 11.0) improved user interfaces and added support for XML data import and export, enhancing interoperability with other systems.
Access 2007 introduced the ACCDB file format, supporting new data types like multi-value and attachment fields. It also adopted the Microsoft Office Ribbon interface, improving user experience. Access 2013 shifted towards web app development, enabling users to create browser-based applications. Subsequent versions, including Access 2016 and beyond, focused on cloud integration, allowing databases to be stored and accessed via Microsoft Azure and SharePoint.
Microsoft Access is widely used for:
Microsofr Access Programmer provide services such as:
When you need an expert Access programmer for your Pasadena, California, business contact us at (323) 285-0939.
Find out more about our Access programming service on the Microsoft Access programmer Pico Rivera, California web page.